44 fluorescent labels and light microscopy
Fluorescence Microscope: Principle, Types, Applications Fluorescence microscopy is a type of light microscope that works on the principle of fluorescence. A substance is said to be fluorescent when it absorbs the energy of invisible shorter wavelength radiation (such as UV light) and emits longer wavelength radiation of visible light (such as green or red light). Fluorescent Dyes | Science Lab | Leica Microsystems In fluorescence microscopy there are two ways to visualize your protein of interest. Either with the help of an intrinsic fluorescent signal - by genetically linking a fluorescent protein to a target protein - or with the help of fluorescently labeled antibodies that bind specifically to a protein of interest.
Introduction to Fluorescence Microscopy | Nikon's MicroscopyU Introduction to Fluorescence Microscopy. The absorption and subsequent re-radiation of light by organic and inorganic specimens is typically the result of well-established physical phenomena described as being either fluorescence or phosphorescence. The emission of light through the fluorescence process is nearly simultaneous with the ...
Fluorescent labels and light microscopy
Light Microscope- Definition, Principle, Types, Parts, Labeled Diagram ... A light microscope is a biology laboratory instrument or tool, that uses visible light to detect and magnify very small objects and enlarge them. They use lenses to focus light on the specimen, magnifying it thus producing an image. The specimen is normally placed close to the microscopic lens. Fluorescence Microscopy - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Fluorescence microscopy is a technique whereby fluorescent substances are examined in a microscope. It has a number of advantages over other forms of microscopy, offering high sensitivity and specificity. In fluorescence microscopy, the specimen is illuminated (excited) with light of a relatively short wavelength, usually blue or ultraviolet (UV). Fluorescent Labelling - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Fluorescence microscopy Fluorescent labeling methods are generally based on reactive derivatives of fluorophores that selectively bind to functional groups contained in target biomolecules and are widely used in biotechnology because of their non-destructive properties and the high sensitivity of fluorescence techniques ( Sahoo, 2012 ).
Fluorescent labels and light microscopy. Fluorescence microscopy: established and emerging methods, experimental ... The primary concern in all forms of microscopy is the generation of contrast; for fluorescence microscopy contrast can be thought of as the difference in intensity between the cell and background, the signal-to-noise ratio. High information-content images can be formed by enhancing the signal, suppressing the noise, or both. Using fluorescence microscopy to shed light on the mechanisms of ... Fluorescence microscopy is one of the most flexible and effective tools to characterize AMPs, particularly in its ability to measure the membrane interactions and cellular localization of peptides. Recent advances have increased the scope of research questions that can be addressed via microscopy through improving spatial and temporal resolution. A Guide to Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy (FLIM) The FLIM method. Fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy ( FLIM) exploits the inherent properties of fluorescent dyes to produce an image. Fluorescent molecules have become essential tools for cell biologists. They are widely used in microscopy to visualize many different structures, targets and dynamic processes within cells, tissues, and ... Fluorescence Microscopy vs. Light Microscopy - Medical News This means that fluorescent microscopy uses reflected rather than transmitted light. For example, a commonly used label is green fluorescent protein (GFP), which is excited with blue light and...
Dots, Probes and Proteins: Fluorescent Labels for Microscopy and Imaging There are currently 20 AlexaFluor dyes which span the excitation spectrum from 346 nm to 784 nm and are available as labelling kits, or conjugated to primary or secondary antibodies. Thermo Scientific produce their own probes called ' DyLight '. The ten probes which are currently available cover a spectrum from 350 nm to 800 nm. Imaging Flies by Fluorescence Microscopy: Principles, Technologies, and ... The development of fluorescent labels and powerful imaging technologies in the last two decades has revolutionized the field of fluorescence microscopy, which is now widely used in diverse scientific fields from biology to biomedical and materials science. ... has brought about the era of fluorescence light microscopy. The first fluorescence ... Different Ways to Add Fluorescent Labels - Thermo Fisher Scientific Using fluorescence provides greater contrast compared to viewing your samples with brightfield microscopy alone. Labeling various targets with separate fluorescent colors allows you to visualize different structures or proteins within a cell in the same experiment. Fluorescence Microscopy - Explanation and Labelled Images A fluorescence microscope works by combining the magnifying properties of the light microscope with fluorescence emitting properties of compounds. Fluorescence microscopy uses a high-intensity light source that excites a fluorescent molecule called a fluorophore in the sample observed. The samples are labeled with fluorophore where they absorb ...
Fluorescent Labeling - What You Should Know - PromoCell Fluorescence microscopy allows the identification of cells and cellular components and the monitoring of cell physiology with high specificity. Fluorescence microscopy separates emitted light from excitation light using optical filters. The use of two indicators also allows the simultaneous observation of different biomolecules at the same time. Fluorescence Microscopy Buyer's Guide | Biocompare: The Buyer's Guide ... Seeing is believing, and for many biologists, what they want to see is fluorescent labels through a microscope. Fluorescence microscopy, which makes it possible to visualize fluorescent proteins or dyes at the cellular and subcellular level, has become a workhorse of modern biology.. The concept of fluorescence, in which a molecule absorbs light of one wavelength and then emits light of a ... Label-free prediction of three-dimensional fluorescence images from ... Label-free prediction of three-dimensional fluorescence images from transmitted-light microscopy. Understanding cells as integrated systems is central to modern biology. Although fluorescence microscopy can resolve subcellular structure in living cells, it is expensive, is slow, and can damage cells. We present a label-free method for predicting ... Fluorescent Labelling - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Fluorescence microscopy Fluorescent labeling methods are generally based on reactive derivatives of fluorophores that selectively bind to functional groups contained in target biomolecules and are widely used in biotechnology because of their non-destructive properties and the high sensitivity of fluorescence techniques ( Sahoo, 2012 ).
Fluorescence Microscopy - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Fluorescence microscopy is a technique whereby fluorescent substances are examined in a microscope. It has a number of advantages over other forms of microscopy, offering high sensitivity and specificity. In fluorescence microscopy, the specimen is illuminated (excited) with light of a relatively short wavelength, usually blue or ultraviolet (UV).
Light Microscope- Definition, Principle, Types, Parts, Labeled Diagram ... A light microscope is a biology laboratory instrument or tool, that uses visible light to detect and magnify very small objects and enlarge them. They use lenses to focus light on the specimen, magnifying it thus producing an image. The specimen is normally placed close to the microscopic lens.

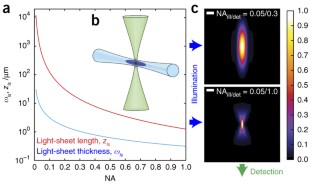
Development a flexible light‐sheet fluorescence microscope for high‐speed 3D imaging of calcium ...











Post a Comment for "44 fluorescent labels and light microscopy"